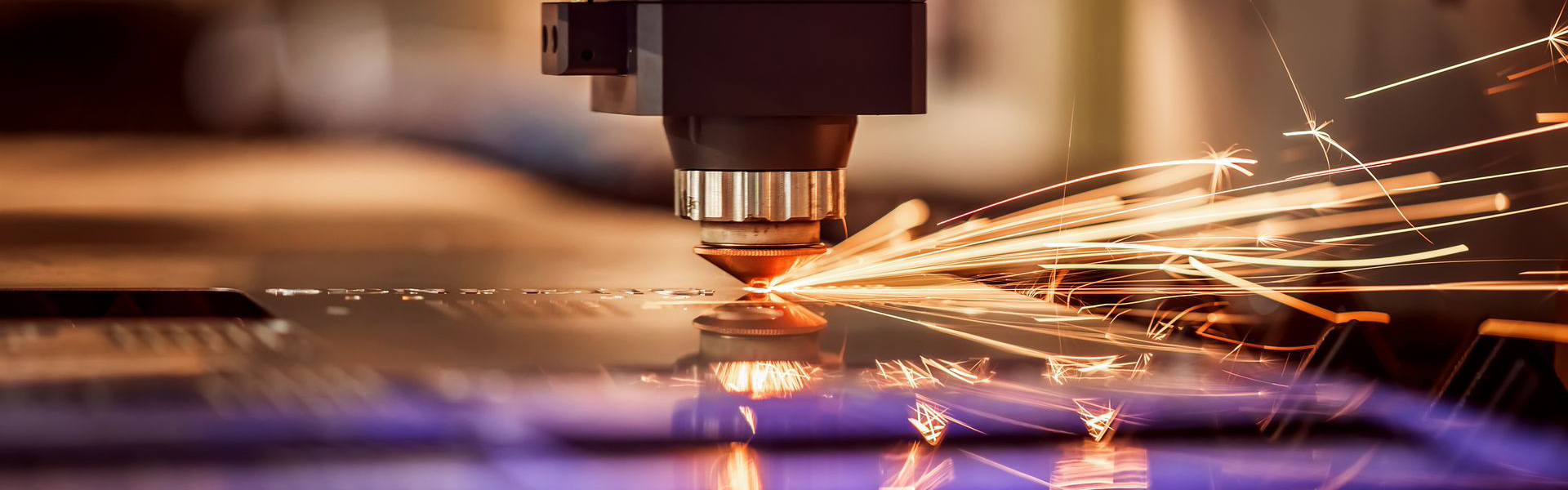
Broaching Machine Automation for Inner Race Processing
Broaching Machine Single-Station Automation for Inner Race Internal Straight Tooth Processing
Introduction: The Demand for High Efficiency and Precision Machining in Manufacturing
With the development of modern manufacturing, enterprises are increasingly demanding higher production efficiency, product quality, and automation levels. Traditional manual operations or semi-automatic equipment can no longer meet the processing needs of high-volume, high-precision parts. Especially in fields such as automotive components, aerospace, and heavy machinery, many key components require complex metal cutting processes, among which broaching is an important machining technique.

1. What is a Broaching Machine? Basic Functions and Principles
1.1 Definition of Broaching Machine
A broaching machine is a type of metal-cutting machine tool primarily used to process complex inner or outer surfaces. It works by moving a multi-toothed cutting tool — known as a broach — along the axial direction of the workpiece, progressively removing material to form the desired geometric shape.
1.2 Classification of Broaching Machines
Depending on the machining method, broaching machines can be categorized into:
Internal broaching machines: Used for machining internal holes, such as internal splines, internal gears, square holes, etc.
External broaching machines: Used for machining external surfaces, such as external splines, guide rails, etc.
Vertical and horizontal broaching machines: Classified based on the direction of broach movement.
1.3 Characteristics of Broaching
Single-stroke complete cutting: Compared with multi-step processes like milling or shaping, broaching completes the entire cutting process in one stroke.
High precision and surface quality: Due to incremental cutting depth per tooth, it achieves high dimensional accuracy and surface finish.
Suitable for mass production: Although the initial investment is relatively high, the short single-piece processing time makes it ideal for large-scale production.
2. Analysis of Challenges in Inner Race and Internal Straight Tooth Machining
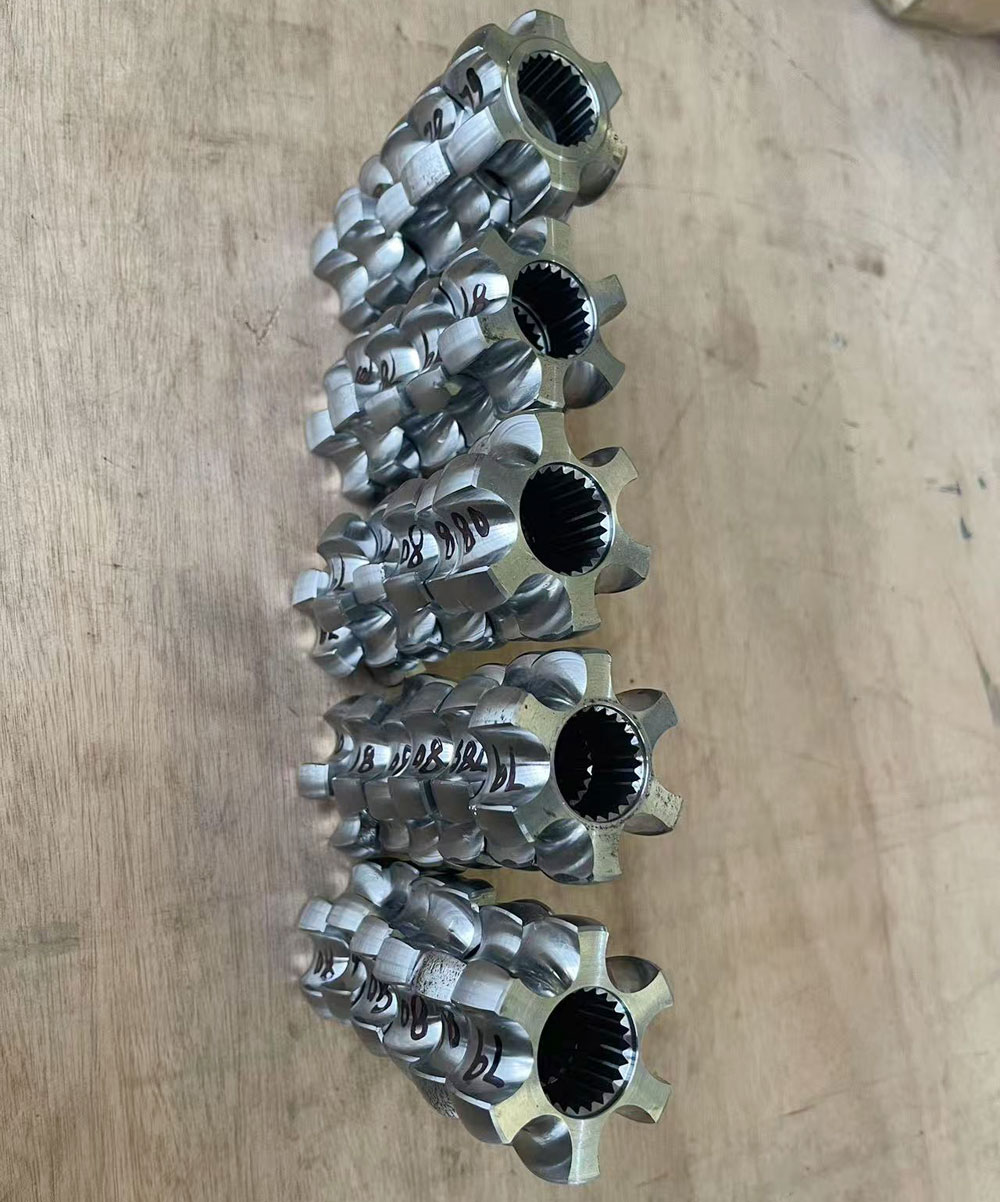
2.1 Introduction to Inner Race
The inner race is a common key component in certain transmission systems, typically used to connect two rotating shafts. It provides good concentricity and torque transmission capability. Its interior is often designed with straight teeth to match other components.
2.2 Traditional Methods for Internal Straight Tooth Machining
Traditional methods for machining internal straight teeth include:
Shaping
Milling
Gear hobbing
Although these methods are feasible, they have limitations in terms of processing efficiency and consistency of precision, especially in mass production scenarios where low efficiency and high human involvement are prominent issues.
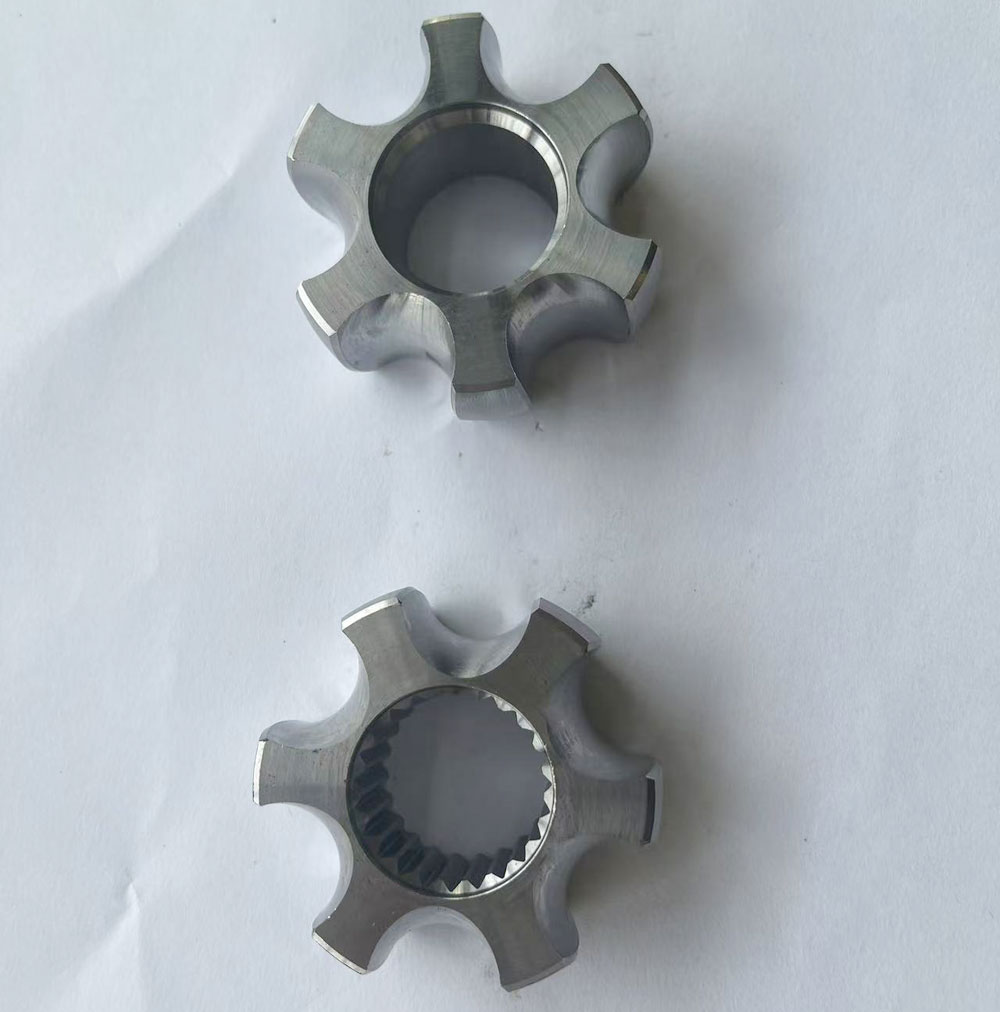

2.3 Advantages of Broaching in Inner Race Machining
Using broaching to process internal straight teeth on inner races offers the following advantages:
One-time forming: No need for multiple clamping or tool changes;
Fast machining speed: A single cycle takes only about 30 seconds;
High precision: Can reach IT6–IT7 grade accuracy;
Strong compatibility with automation: Easy to integrate into fully automated production lines.

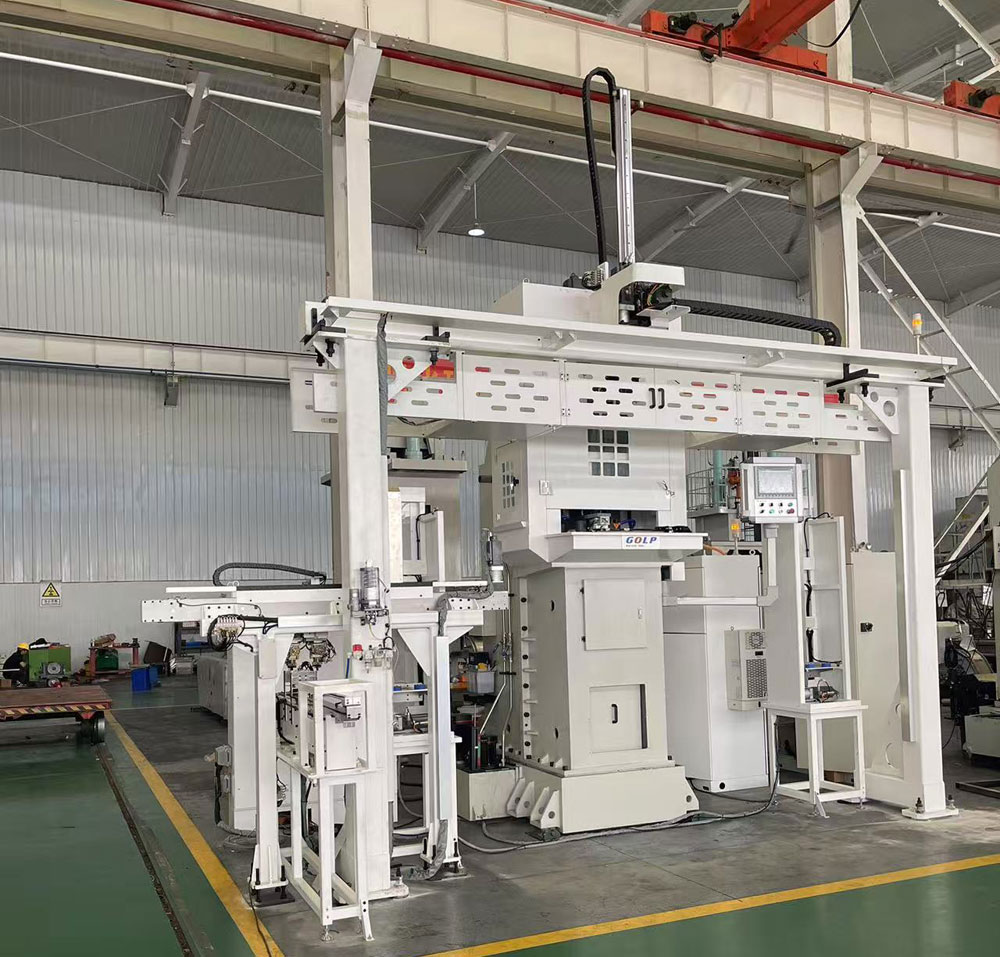
3. Introduction and Advantages of Automated Broaching Machines
3.1 Concept of Automated Broaching Machines
An automated broaching machine is an intelligent device built upon traditional broaching machines by adding features such as automatic loading/unloading, automatic inspection, automatic lubrication, and automatic compensation. Its core goal is to achieve full automation from raw materials to finished products, reducing human intervention and improving production efficiency and stability.
3.2 Functional Features of Automated Broaching Machines
Automatic Loading/Unloading: Automatically transports workpieces to the machining position via robotic arms or conveyors;
Automatic Clamping and Positioning: Ensures consistent positioning during each machining cycle;
Intelligent Control System: Monitors parameters such as broaching force, temperature, and displacement in real-time;
Fault Self-Diagnosis: Equipped with self-check and alarm functions to reduce downtime;
Data Acquisition and Analysis: Supports Industry 4.0 data interfaces for remote monitoring and maintenance.
4. Application of Gantry Robots in Automated Broaching Machines
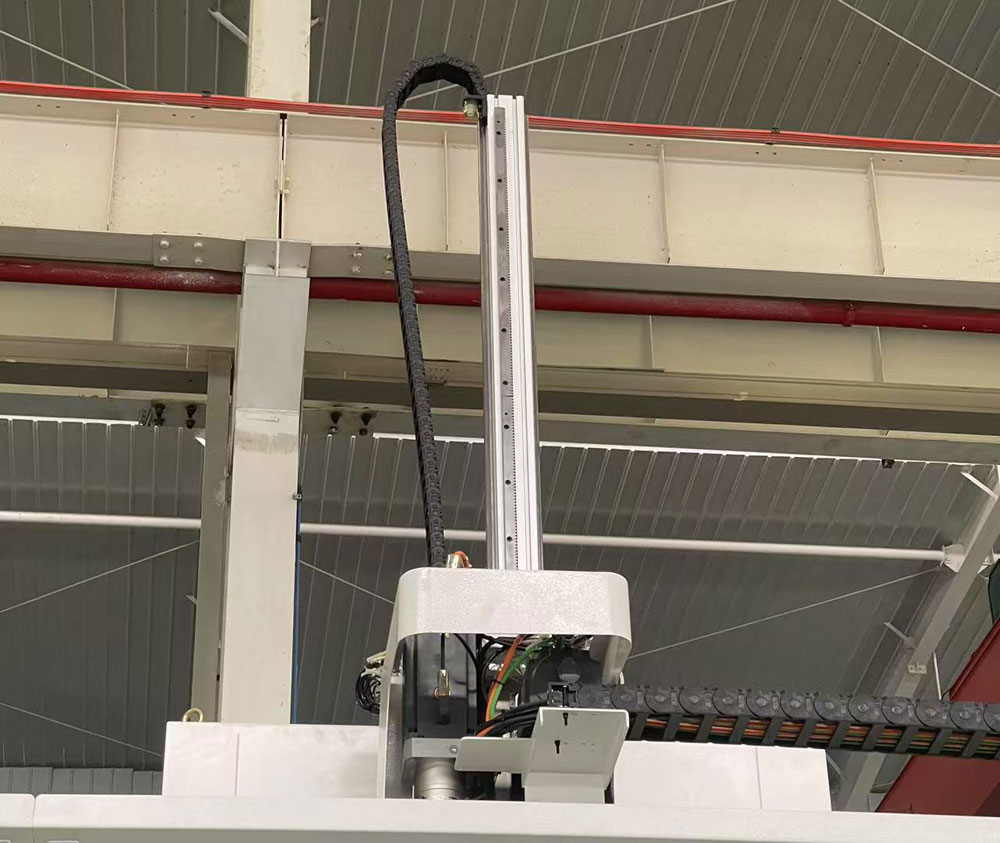
4.1 Basic Concept of Gantry Robots
Gantry robots, also known as portal robots, are automated handling devices installed on X-Y-Z three-axis linear guides. They can move freely within a defined spatial range to perform tasks such as gripping, transporting, and placing objects, and are widely used in automated production lines.
4.2 Roles of Gantry Robots in Broaching Machines
In an automated broaching system, gantry robots mainly perform the following tasks:
Automatic Loading/Unloading:
Pick up the inner race blank from the storage bin and place it into the broaching machine fixture;
After machining, remove the finished part and place it into the finished goods area.
Multi-Station Collaborative Operation:
Can serve multiple broaching machines simultaneously, achieving centralized control and scheduling;
While the broaching machine is operating, the gantry robot can prepare the next workpiece, enabling seamless operation.
Precise Positioning and High Repeatability:
Gantry robots offer repeat positioning accuracy within ±0.05 mm, ensuring consistency in clamping;
This is particularly important for precision machining such as internal straight teeth.
Safety Protection and Environmental Adaptability:
Capable of stable operation in harsh environments such as high temperatures and dust;
Equipped with safety enclosures and light curtains to ensure safe human-machine separation.
4.3 Structure of a Typical Gantry System
A typical gantry system consists of the following components:
X/Y/Z axis linear guides and servo motors: Responsible for spatial positioning;
End-effectors (mechanical grippers or vacuum suction cups): Used for workpiece handling;
PLC controller and HMI interface: Enables program control and human-machine interaction;
Safety sensors and emergency stop devices: Ensure operational safety.

5. Detailed Process Description: From Loading to Unloading in Full Automation
5.1 Overview of the Process Flow
Loading Phase: The gantry robot picks up the inner race blank from the storage bin;
Positioning and Clamping: The workpiece is placed into the broaching machine fixture and automatically clamped;
Broaching Process: The broach moves along the inner hole direction to complete the formation of straight teeth;
Cooling and Chip Removal: Automatic oil spraying for cooling and chip removal;
Unloading Phase: The gantry robot removes the finished part and sends it to the next process;
Inspection Feedback: Optional online detection system can inspect machining dimensions.
6. Economic Benefits and Industry Application Prospects
6.1 Cost-Benefit Analysis
Although the initial investment for automated broaching machines and gantry systems is relatively high, their long-term benefits far outweigh the costs:
Reduced labor costs: Reduces the number of operators required;
Lower scrap rate: Automation minimizes human error;
Increased productivity: Thousands of parts can be processed daily;
Long equipment life: Both broaching machines and gantry systems are durable with low maintenance costs.
6.2 Industry Application Prospects
Currently, automated broaching machines and gantry systems are widely applied in the following fields:
Automotive Component Manufacturing: Such as transmission housings, universal joint inner races, etc.;
Aerospace: High-precision gears, bearing seats, etc.;
Heavy Machinery: Hydraulic pump housings, couplings, etc.;
Power Tools and Home Appliances: Small gears, shaft parts, etc.
In the future, with the development of smart manufacturing and Industry 4.0, automated broaching machines and gantry systems will further integrate AI, big data, and IoT technologies, achieving more efficient and intelligent production modes.
7. Conclusion: Moving Toward a New Era of Intelligent Manufacturing
The integration of automated broaching machines and gantry systems not only solves the efficiency bottleneck in internal straight tooth machining of inner races but also provides a brand-new solution for the manufacturing industry. From manual operation to fully automated unmanned production, this is not just an equipment upgrade, but a transformation in manufacturing philosophy and technical systems.
In the future, with the continuous emergence of new materials and new processes, broaching technology will continue to evolve, with applications such as high-speed broaching, dry broaching, and composite broaching bringing new vitality to this traditional process.