Gear Cutting Methods Explained : Gear Hobbing to Grinding
Gear Cutting Methods Explained: Hobbing to Grinding
Gear cutting methods form the technical foundation of the entire gear manufacturing industry. Whether producing reduction gearboxes, automotive transmissions, wind power drives, or heavy equipment components, every gear must pass through a precise cutting and finishing process before it can operate reliably.
In modern factories, gear accuracy is no longer optional. Even micron-level errors in tooth profile or pitch spacing can lead to noise, vibration, excessive heat, and shortened service life. As performance standards continue to rise, manufacturers are moving away from traditional manual machining and adopting CNC gear cutting machines and automated production lines.
This article explains the major gear cutting methods-gear hobbing, shaping, milling, and grinding-and shows how these processes work together to build an efficient gear manufacturing system.

What Is Gear Cutting?
Gear cutting is the controlled removal of metal from a blank to create precise gear teeth with defined geometry. Unlike ordinary machining, gear cutting requires synchronized motion between the tool and the workpiece to generate the involute tooth profile.
The process determines:
Module accuracy
Tooth spacing
Profile error
Surface finish
Contact ratio
These parameters directly affect gearbox performance and durability.
Because of this complexity, most manufacturers rely on dedicated CNC gear machines rather than general-purpose equipment.

Why Gear Accuracy Is Critical?
Many engineers underestimate how sensitive gear systems are.
For example:
10-20 μm profile error → increased noise
Poor surface finish → faster wear
Inconsistent pitch → vibration
Incorrect backlash → overheating
In reduction gearboxes or precision drives, these issues can lead to early failure.
Therefore, modern gear manufacturing emphasizes not only cutting speed but also precision and stability. This is why advanced gear cutting machines and grinding machines are essential.
Method 1: Gear Hobbing (Core Production Process)
Principle of Gear Hobbing
Gear hobbing is the most widely used gear cutting method worldwide. A rotating hob cutter gradually generates the tooth profile while the workpiece rotates at a synchronized speed.
Unlike milling, which cuts one tooth at a time, hobbing is continuous. This makes it extremely efficient for large scale production.

Advantages of Gear Hobbing
High productivity
Continuous cutting motion
Excellent repeatability
Lower cost per part
Suitable for automation
For factories producing hundreds or thousands of gears daily, gear hobbing is usually the first choice.
CNC Gear Hobbing Machines in Practice
Modern CNC gear hobbing machines offer:
Multi-axis control (4-6 axis)
High-rigidity cast structure
Automatic tool change
Servo-driven spindles
Online measurement
Automatic loading systems
These features ensure both speed and accuracy.
G150 G350 G500 CNC Gear Hobbing Machine
Such machines are widely used in gearbox and transmission factories where consistent quality is critical.
Method 2: Gear Shaping (Internal Gear Specialist)
Gear shaping is particularly useful when cutting internal gears or gears close to shoulders where hobbing cannot reach.
A reciprocating cutter moves vertically while rotating with the workpiece, gradually shaping the tooth form.
When to Use Gear Shaping?
Ideal for:
Internal ring gears
Planetary carriers
Small-batch production
Complex geometries
Although slower than hobbing, shaping provides unmatched flexibility.
GS200 GS400 GS800 Gear Shaping Machine

Most gearbox manufacturers combine shaping and hobbing in the same production line.
Method 3: Gear Milling (Flexible and Prototyping)
Gear milling uses a form cutter to machine teeth individually.
While less efficient, it remains useful for:
Prototypes
Repairs
Small orders
Special tooth forms
CNC milling centers provide flexibility when dedicated gear machines are unnecessary.
Method 4: Gear Grinding (Precision Finishing)
After heat treatment, gears may warp slightly. Grinding corrects these distortions and achieves final accuracy.
Benefits of Grinding
Very high precision (DIN 5-6 or better)
Smooth surface finish
Reduced noise
Extended life
Grinding is essential in:
Automotive gears
High end reducers
Aerospace drives
Profile/ worm wheel Gear Grinding Machine

Without grinding, high-performance gearboxes cannot meet modern standards.
Integrating Methods into a Gear Production Line
In real manufacturing, gear cutting methods are rarely used alone.
A typical workflow:
Hobbing (rough cutting);
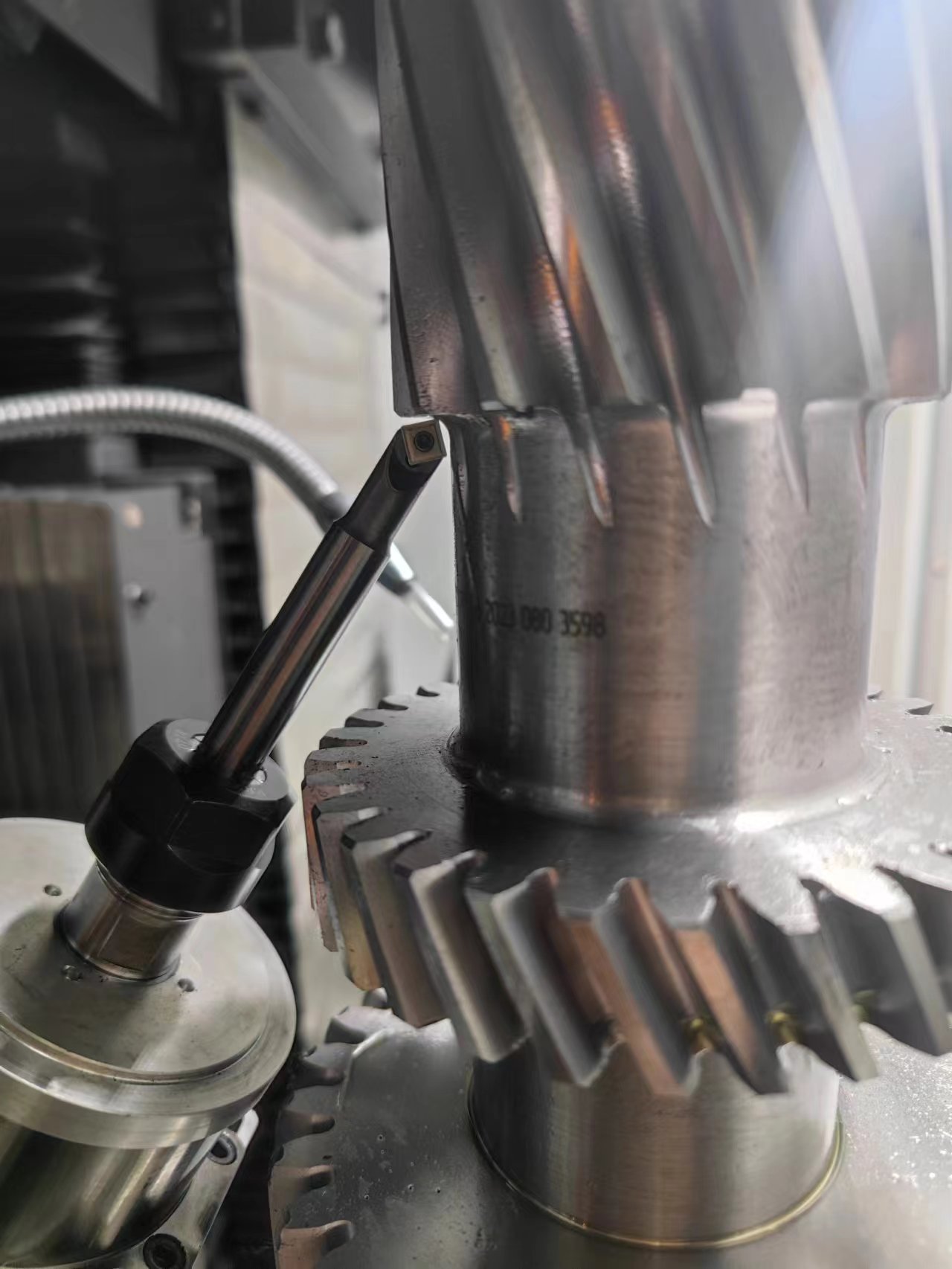


Grinding (finishing);
Inspection
This integrated approach improves both speed and quality.
Automated Gear Production Line

How to Choose the Right Gear Cutting Equipment?
When selecting gear machines, consider:
Production volume
Gear type
Required precision
Budget
Automation level
A balanced combination of CNC gear hobbing machines, shaping machines, and grinding machines usually provides the best results.
Conclusion
Different gear cutting methods serve different purposes. Understanding their strengths helps manufacturers design efficient production systems.
By combining advanced CNC gear machines with smart automation, modern factories can achieve both high output and precision-- the key to competitive gear manufacturing.