How does a tool grinder work?
A tool grinder is a precision machining equipment mainly used to repair or manufacture metal cutting tools such as drills, milling cutters and turning tools. It removes material by grinding to achieve the desired geometry and surface roughness required. The working principle of a tool grinder involves several aspects.
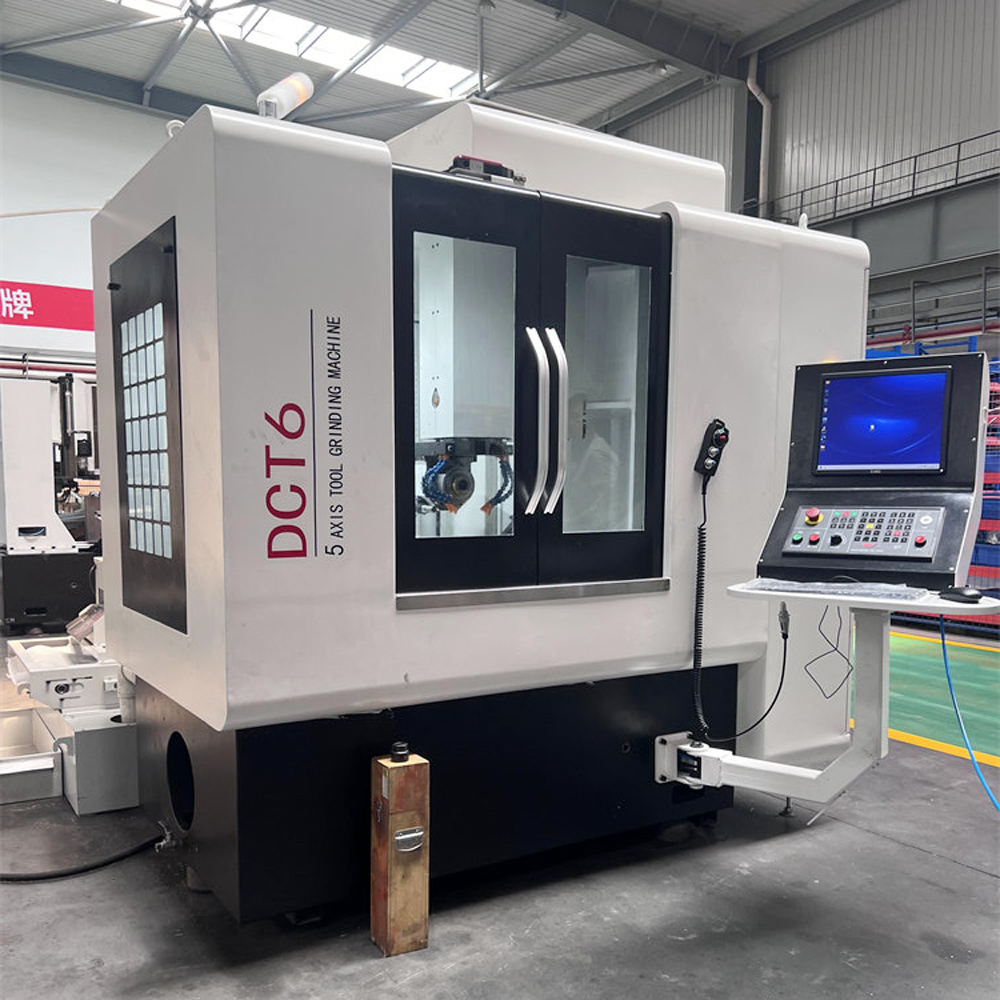

Principle of operation
At the heart of a tool grinder is a high-speed rotating grinding wheel, the surface of which consists of a number of tiny abrasive grains that come into contact with the workpiece at high speeds, removing material from the surface of the workpiece by friction. In order to ensure machining accuracy, tool grinding machines are usually equipped with a precision guideway system and a high-precision positioning device, which can accurately control the relative position and movement trajectory between the grinding wheel and the workpiece.
Machining the workpiece
During the machining process, the workpiece is firmly fixed on the table while the grinding wheel moves along a predetermined path for grinding. Depending on the machining requirements, the grinding wheels can be of different shapes and materials, such as flat grinding wheels for flat surfaces and profile grinding wheels for complex shaped tools. In addition, coolant is used to reduce the temperature of the grinding process and to carry away debris in order to improve the efficiency and quality of the grinding process.
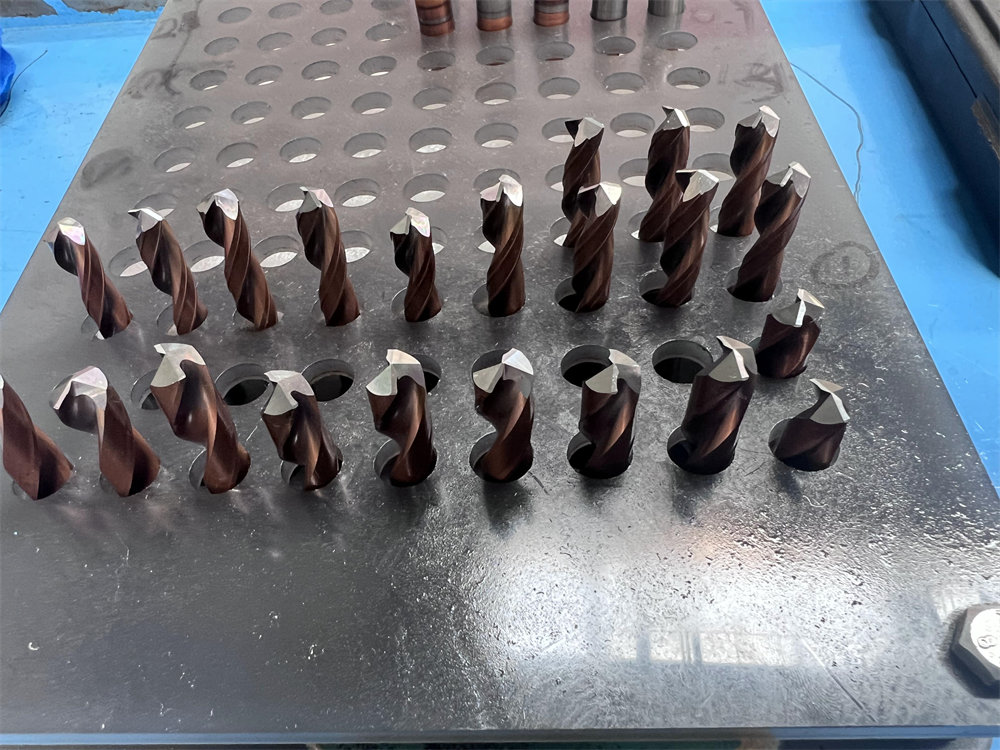

Fields of Application
Tool grinding machines are widely used in a variety of manufacturing industries, including aerospace, automotive, and mold making. With the advancement of technology, modern tool grinders are not only able to realize automated production, but also capable of multi-axis linkage processing of complex tools, which greatly improves production efficiency and product quality.
In summary, through its unique grinding technology and precision control system, tool grinder provides indispensable support for industrial production while ensuring high precision, which is of great significance for enhancing the competitiveness of the entire manufacturing industry.